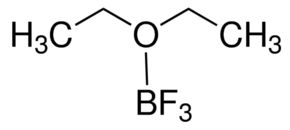
Boron Trifluoro Etherate
Product Details:
Boron Trifluoro Etherate Price And Quantity
- 1000 Kilograms
- 1000 INR/Kilograms
Boron Trifluoro Etherate Trade Information
- 1000 Kilograms Per Week
- 1 Week
- Yes
- Contact us for information regarding our sample policy
Product Description
Boron trifluoro etherate BFOEt is a chemical compound composed of boron trifluoride BF complexed with diethyl ether OEt It is commonly used as a Lewis acid catalyst in organic chemistry for various reactions due to its strong electronaccepting properties
Key Characteristics
Chemical Formula BFOCH
Molecular Weight 14193 gmol
Appearance Colorless liquid
Boiling Point Around 126C
Solubility Soluble in common organic solvents
1 Lewis Acid Catalyst
Role BF etherate is widely used as a Lewis acid meaning it accepts electron pairs from electron donors Its strong electrophilicity makes it an excellent catalyst in various organic transformations
Common Applications
FriedelCrafts Acylation and Alkylation BF etherate is often used to catalyze these reactions which are important in the formation of carboncarbon bonds in the synthesis of aromatic compounds
Polymerization It can be used as a catalyst in polymerization reactions particularly in the polymerization of olefins and other unsaturated compounds
2 Organic Synthesis Applications
Esterification and Transesterification BF etherate is commonly used to promote the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols or in transesterification reactions
Aldol Condensation It is sometimes used in aldol condensation reactions where carboncarbon bonds are formed between aldehydes or ketones and enolizable carbonyl compounds
Dehydration Reactions As a strong acid it can assist in dehydration reactions facilitating the removal of water and driving condensation reactions to completion
3 Selective Reaction Control
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity BF etherate often provides better control over regio and stereoselectivity in complex organic transformations making it an important tool in synthesizing specific isomers of organic molecules
4 Stability and Handling
Storage Boron trifluoro etherate is sensitive to moisture as it can hydrolyze upon contact with water releasing boron trifluoride gas BF and potentially generating hydrofluoric acid HF Therefore it must be stored in airtight containers and handled in a dry environment
Decomposition Hydrolysis in moist conditions can lead to the formation of corrosive and toxic byproducts like boric acid and hydrogen fluoride
5 Safety Considerations
Toxicity BF etherate is corrosive and toxic particularly to the respiratory system Inhalation of vapors or direct skin contact should be avoided and proper personal protective equipment PPE should be used
Handling Work in wellventilated areas and avoid exposure to moisture to prevent the release of harmful gases
Properties Recap
Lewis Acid Strength BF etherate is a very strong Lewis acid commonly used for reactions requiring electron pair acceptance
Reaction Control It offers good control over reaction selectivity and is highly effective in acidcatalyzed processes
Moisture Sensitivity It should be handled carefully to avoid degradation and hazardous byproducts
BF etherate is a key reagent in organic and industrial chemistry prized for its versatility in catalysis and ability to promote a wide range of reactions with precision

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+